Beyond the Acronyms: Exploring QA and QC
Introduction
In the world of product and service development, ensuring high quality is paramount. However, many people often confuse Quality Assurance (QA) with Quality Control (QC). This blog aims to demystify the differences between quality assurance and quality control, highlighting their distinct roles, activities, and importance. Understanding the Quality Assurance vs Quality Control debate is crucial for businesses striving for excellence.
Quality Assurance Definition (QA)
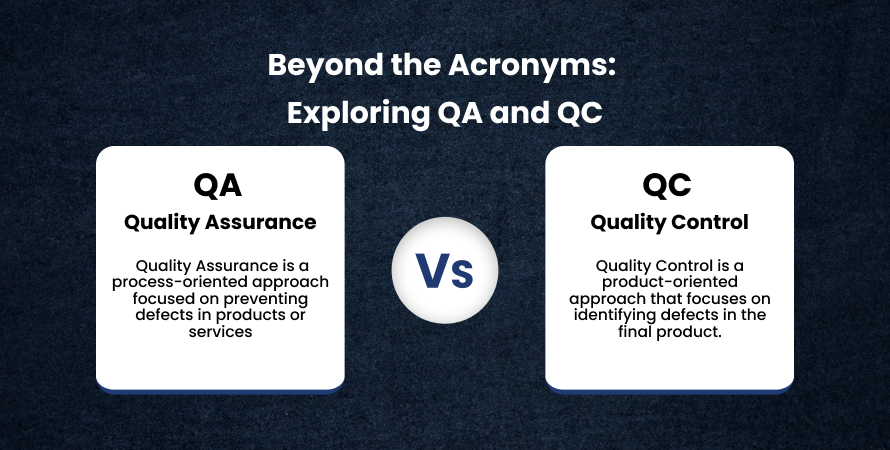
QA meaning Quality Assurance is a process-oriented approach focused on preventing defects in products or services. QA assurance ensures that the processes used in creating a product are followed correctly and systematically to maintain the desired quality level. It’s about setting up a good quality management system and ensuring that it is followed.
Key Components Include:
- Standards and Procedures: Establishing clear standards and procedures that guide the production process.
- Documentation: Keeping thorough documentation to track process adherence and improvements.
- Audits: Conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with established standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing ongoing improvements to processes based on feedback and performance data.
Examples of QA activities include creating plans that outline quality goals and procedures, conducting internal audits to ensure processes are being followed and making changes to enhance efficiency and product quality.
Quality Control Definition (QC)
QC, Quality Control is a product-oriented approach that focuses on identifying defects in the final product. QC meaning is all about the operational techniques and activities used to fulfill requirements for quality. Unlike QA, which is proactive, QC is reactive, aimed at identifying and correcting defects.
Key Components of QC
- Testing and Inspection: Evaluating the product through various tests and inspections to detect defects.
- Measurement and Analysis: Using data to understand defect patterns and their causes.
- Corrective Actions: Implementing measures to correct defects and prevent their recurrence.
For example, conducting product inspections, testing samples to ensure they meet quality standards and analyzing defect trends.
Quality Control VS Quality Assurance
Understanding the differences between Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) is fundamental for effective quality management. Although both aim to ensure product quality, they approach it from different angles. Here, we delve deeper into quality control vs assurance the distinct focuses, activities, and responsibilities that set QC and QA apart.
Focus and Goals
Quality Assurance is primarily concerned with the processes used to create a product. QA is proactive, aiming to prevent defects before they occur by ensuring that processes are well-defined, consistently followed, and continuously improved. The ultimate goal of Q A is to enhance and stabilize production processes to avoid the creation of defective products.
- Prevention Over Detection: QA emphasizes preventing issues through proper process design and implementation.
- Consistency and Efficiency: Ensuring that processes are efficient and yield consistent results.
- Long-Term Improvements: Focus on long-term process improvements rather than immediate fixes.
In contrast, Quality Control is centered on the final product. QC is reactive as its main aim is to identify and correct defects after the product has been developed. The primary goal of QC is to detect and eliminate defects to ensure that the final product meets the required standards and specifications.
- Detection and Correction: QC identifies defects in the final product and takes corrective actions.
- Short-Term Solutions: Focus on immediate correction of identified issues.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring that the product meets customer expectations and regulatory standards.
Activities Involved
The activities involved in QA and QC reflect their different focuses.
Quality Assurance Activities includes:
- Developing comprehensive quality management plans that outline quality goals, standards, and procedures.
- Keeping detailed records of processes, standards, and compliance to ensure traceability and accountability.
- Conducting regular audits to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and efficiently.
- Providing continuous training to employees to maintain high standards of process execution and understanding.
- Implementing a cycle of feedback and improvement to enhance processes over time, often using methodologies like Six Sigma or Total Quality Management (TQM).
Quality Control Activities includes:
- Performing rigorous testing and inspection of products at various stages of production to detect defects.
- Using statistical methods to sample products and identify defect patterns.
- Measuring product characteristics against predefined standards and analyzing data to understand defect causes.
- Taking immediate corrective actions to fix defects and prevent them from recurring in future production.
- Keeping records of identified defects and corrective actions taken to track trends and improve future quality.
Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities in QA and QC differ significantly, with each focusing on different aspects of quality management.
Quality Assurance Roles includes:
- Responsible for designing and implementing quality management systems and processes.
- Conducting audits to ensure compliance with established procedures and standards.
- Providing ongoing training to employees to ensure they understand and follow quality processes.
- Identifying opportunities for process improvements and implementing changes.
Quality Control Roles includes:
- Conducting tests and inspections to identify defects in the final product.
- Designing and implementing testing protocols to ensure product quality.
- Analyzing defect data to identify trends and root causes.
- Managing the process of fixing defects and implementing corrective actions.
For example, in a manufacturing setting, QA might involve developing a detailed quality management plan that outlines the processes for assembling a product. This plan includes standards, procedures, and documentation requirements. QA, Quality Assurance teams conduct regular audits to ensure that these processes are followed correctly and efficiently.
In contrast, QC involves inspecting the final products to identify any defects that may have occurred during assembly. QC teams perform tests and analyze defect data, which can then be used to refine and improve the processes defined by QA.
Hence, after analyzing the section related to QA vs QC it is clear that clear definitions and communication of QA and QC roles are essential to avoid overlap and ensure that both functions operate effectively. Organizations should establish distinct responsibilities and ensure that all team members understand their specific roles in the quality management process.
How QA and QC Complement Each Other
While QA and QC have distinct roles, their integration is crucial for a comprehensive quality management system. QA ensures that processes are set up correctly and efficiently, while QC ensures that the final product meets quality standards. Together, they form a feedback loop where QC findings inform QA improvements, creating a cycle of continuous quality enhancement. So, whether it is quality control or assurance, both stand of equal importance for a business’ growth.
Integrated Approach
While QA and QC have distinct roles, they are complementary. QA sets up the processes that QC monitors and improves. Together, they form a comprehensive quality management system.
Cycle of Quality
The QA and QC feedback loop ensures continuous improvement. QA plans and establishes processes; QC inspects and identifies defects, leading to further refinements in QA.
Case Studies/Examples
Real-world examples include the automotive industry, where QA ensures assembly processes are robust, while QC tests vehicles for defects before they reach customers.
Importance in Different Industries
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, QA ensures that production processes are consistent, efficient, and adhere to industry standards. This helps prevent defects from occurring, saving time and costs associated with rework. QC, on the other hand, is crucial for inspecting and testing final products to ensure they meet quality specifications. Together, QA and QC help maintain product reliability and safety, essential for customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance.
Software Development
In software development, QA involves planning and executing processes to ensure software is developed according to specified requirements and standards. This includes code reviews, design inspections, and process audits. Software QA or Software Quality Assurance (SQA) aims to prevent bugs and ensure code quality. QC, or software testing, detects and fixes bugs before the software reaches the user. This dual approach ensures the software is functional, reliable, and user-friendly.
Healthcare
In healthcare, QA ensures that clinical procedures, protocols, and processes meet stringent regulatory standards and best practices, thus preventing errors in patient care. QC involves testing medical products, devices, and laboratory results to ensure they meet safety and efficacy standards. This ensures patient safety, enhances treatment outcomes, and maintains compliance with health regulations. Combining QA and QC helps in delivering high-quality patient care and improving healthcare services.
These explanations illustrate how both QA and QC are indispensable in various industries, ensuring processes and products meet the highest standards of quality.
Challenges and Best Practices
Various common challenges include overlapping of roles of both QA and QC because of confusion in responsibilities, adequate allocation of roles and responsibilities while maintaining consistency in quality.To cope up with the challenges best measures include being precise with the roles of each by providing regular updates and training.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between QA and QC is crucial for effective quality management. QA focuses on preventing defects by ensuring robust and efficient processes, while QC focuses on identifying and correcting defects in the final product.
By integrating QA and QC, organizations can create a comprehensive quality management system that not only prevents defects but also ensures that final products meet the highest standards of quality. This integrated approach ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and long-term success.